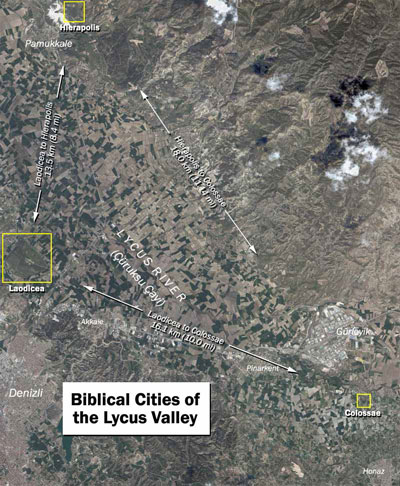
The church at Colossae was formed during Paul’s ministry in Ephesus. A Colossian named Epaphras traveled to Ephesus (125 miles NW of Colossae) and heard Paul preach the gospel. In returning home Epaphras shared the message with his hometown and the church at Colossae was born. “Epaphras had earlier journeyed to Paul to help him in whatever way he could, representing the three churches of the Lycus valley (Laodicea, Hierapolis, Colossae)”.1
Epaphras is with Paul (Currently jailed in Ephesus) and has given Paul news of problems in the church in Colossae. Paul writes his Colossians epistle to address these problems.
I favor Pauline authorship of Colossians and Philemon while Paul was jailed in Ephesus ~54 A.D. I don’t think he wrote these epistles in Rome (or Caesarea) for three reasons:
- Onesimus, a slave who escaped from his owner Philemon in Colossae, is unlikely to have been able to make two (Or three) trips to Rome from his home in Colossae.
- “…it seems unlikely that, having seen Rome as a staging-post on the way to Spain (Rom. 15:22–29), Paul would be hoping to visit Philemon soon after his impending release.”2
- The epistle contains advice more likely to be needed by a very young church than a church that had been grappling with such issues for eight or nine years.3
If Paul wrote Colossians while in Ephesus both the church, and Paul, were ~nine years younger than widely presumed: Paul is in his early 50’s and the church is barely a year old. That Paul describes himself as an “old man” in Philemon is still consistent with the hard life he’d lived until then.
The letters to the Colossians and to Philemon (And possibly Ephesians) were carried to their recipients by Tychicus and Onesimus with the latter being returned by Paul to his owner, Philemon. Philemon’s house is being used as a church in Colossae and Paul is hoping to persuade him to look favorably on his former slave, Onesimus, who became a Christian during his time with Paul.
Did Paul Write Colossians?
I find the arguments that someone other than Paul wrote the letter, unconvincing. In making their case, the non-Pauline authorship camp makes at least two faulty assumptions:

- That a brilliant writer such as Paul could not, or would not, adapt his writing style and vocabulary with respect to the intention, problems and recipients of the letter. To the contrary: Anyone capable of writing Colossians has proven themselves capable of adjusting language and style to the widest audience possible. In fact, each of these Epistles continues to communicate quite effectively with the entire world since they were written. Putting aside, for now, the fact that his writing was divinely inspired, I’m not aware of any writer having achieved a greater feat (Socrates, Plato, Shakespeare, etc.).
- That literary genius and spectacular writing abilities can somehow be perfectly mimicked or obtained by extensive study or “Spending lots of time” with the author. I would think a comparison of the epistles of Timothy to those of Paul’s would end such an argument. For those still unconvinced, rest assured that, no matter how long you might have been able to hang out with Shakespeare you still wouldn’t be able to write one of his plays.
Earthquakes in Laodicea and Colossae:
“Sometimes one also hears the argument that Paul could not have written to Colossae from Rome as late as A.D. 62 because the city of Colossae was destroyed by an earthquake in that year. This is confusing the earthquake which struck Laodicea in A.D. 60–61 with the earthquake which hit Colossae in A.D. 64. It is unfortunate that while Laodicea has undergone a good deal of archaeological work in recent years, Colossae still remains one of the NT sites which has never been excavated. Work would need to be done there before we could begin to assess the effects of the earthquake on that small town.”4
Laodicea and Colossae are only 10 miles apart. An earthquake capable of doing damage to one would be felt in both cities and probably do the same amount of damage. If Paul had written Colossians in 62 A.D. it would be remarkable for him to refrain from mentioning a Laodicean earthquake that happened one year prior. The second 64 A.D. quake in Colossae does not inform the the dating of the epistle, at all.
Lost Epistle to Laodicea
In Colossians 4, Paul asks the Colossians and Laodiceans to read each other’s letters. It’s highly probably that an epistle written to the Laodiceans has been lost.
Colossians Outline5
Doctrine: Christ’s Preeminence Declared
- Greeting (1:1–2)
- Thanksgiving (1:3–8)
- Prayer (1:9–14)
- Praise to Christ (1:15–20)
a) Christ is Lord of creation ( 1: 15–17)
b) Christ is Lord of redemption ( 1: 18–20) - Reconciliation of the Colossians to God ( 1: 21–23)
- The Apostle Paul’s Labor for the Gospel ( 1: 24–2: 3)
a) Paul’s suffering and stewardship of the mystery ( 1: 24–28)
b) Paul’s labor for the Colossians ( 1: 29–2: 3)
Danger: Christ’s Preeminence Defended
- The Dangerous Teaching at Colossae ( 2: 4–23)
a) Warning about a deceptive teaching ( 2: 4–8)
b) Help for the danger: resources in Christ ( 2: 9–15)
c) Additional warnings about the teaching ( 2: 16–23)
Duty: Christ’s Preeminence Demonstrated
- The Proper Focus: Christ and the Life Above ( 3: 1–4)
- Instructions on Living the Christian Life ( 3: 5–4: 6)
a) Dealing with the sins of the past ( 3: 5–11)
b) Putting on the virtues of Christ ( 3: 12–17)
c) Living in the Christian household ( 3: 18–4: 1)
d) Persistence in prayer ( 4: 2–4)
e) Good behavior toward those outside the community ( 4: 5–6) - Personal Greetings and Instructions ( 4: 7–17)
a) Remarks about the messengers carrying the letter ( 4: 7–9)
b) Greetings from Paul’s associates ( 4: 10–14)
c) Greetings to the Christians in Laodicea ( 4: 15–17) - Letter Closing ( 4: 18)
- Melick, R. R. (1991). Philippians, Colossians, Philemon (Vol. 32, p. 165). Nashville: Broadman & Holman Publishers. ↩
- Wright, N. T. (1986). Colossians and Philemon: an introduction and commentary (Vol. 12, p. 38). Downers Grove, IL: InterVarsity Press. ↩
- Wright, N. T. (1986). Colossians and Philemon: an introduction and commentary (Vol. 12, p. 40). Downers Grove, IL: InterVarsity Press. ↩
- Witherington, B., III. (2007). The letters to Philemon, the Colossians, and the Ephesians : a socio-rhetorical commentary on the captivity Epistles (p. 19). Grand Rapids, MI: Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing Co. ↩
- ESV Study Bible ↩